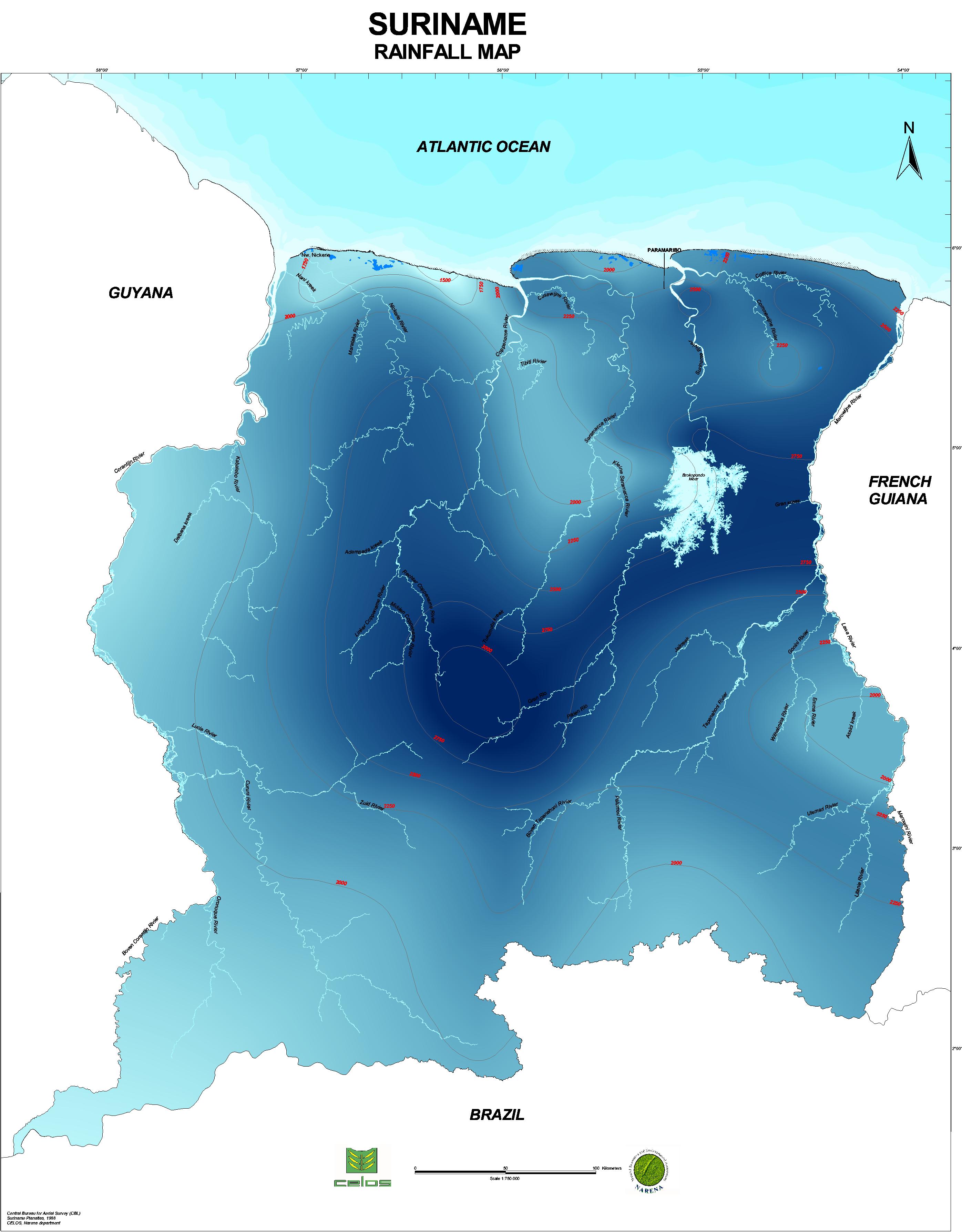
Suriname is located on the north-east coast of South America (appr. 54o-58o WL and 2o-6o NL) and has an area of about 156,000 km2. The climate is tropical, with daily temperatures varying between 23 and 31 degrees Celsius (ºC). The relative humidity is about 80% a year, the sunshine is about 58% a year (1931-1960). The average annual rainfall in Paramaribo is about 2,200 millimeters. In the whole country, the rainfall varies from less than 1,750 to greater than 3,000 millimeters annually. The annual evaporation is about 1,700 mm (1931-1960). About 67% of the precipitated water on the Suriname rivers basins returns to the atmosphere by evapotranspiration and approximately 33% is drained off into the Atlantic ocean. The year can be roughly divided in two wet seasons (April to mid-August and December to February) and two dry seasons (February to April and mid-August to December). According to the Water Poverty Index (WPI), Suriname belongs to the top 10 water-rich nations in the world are (World Water Council, 3rd World Water Forum, 2002).

General
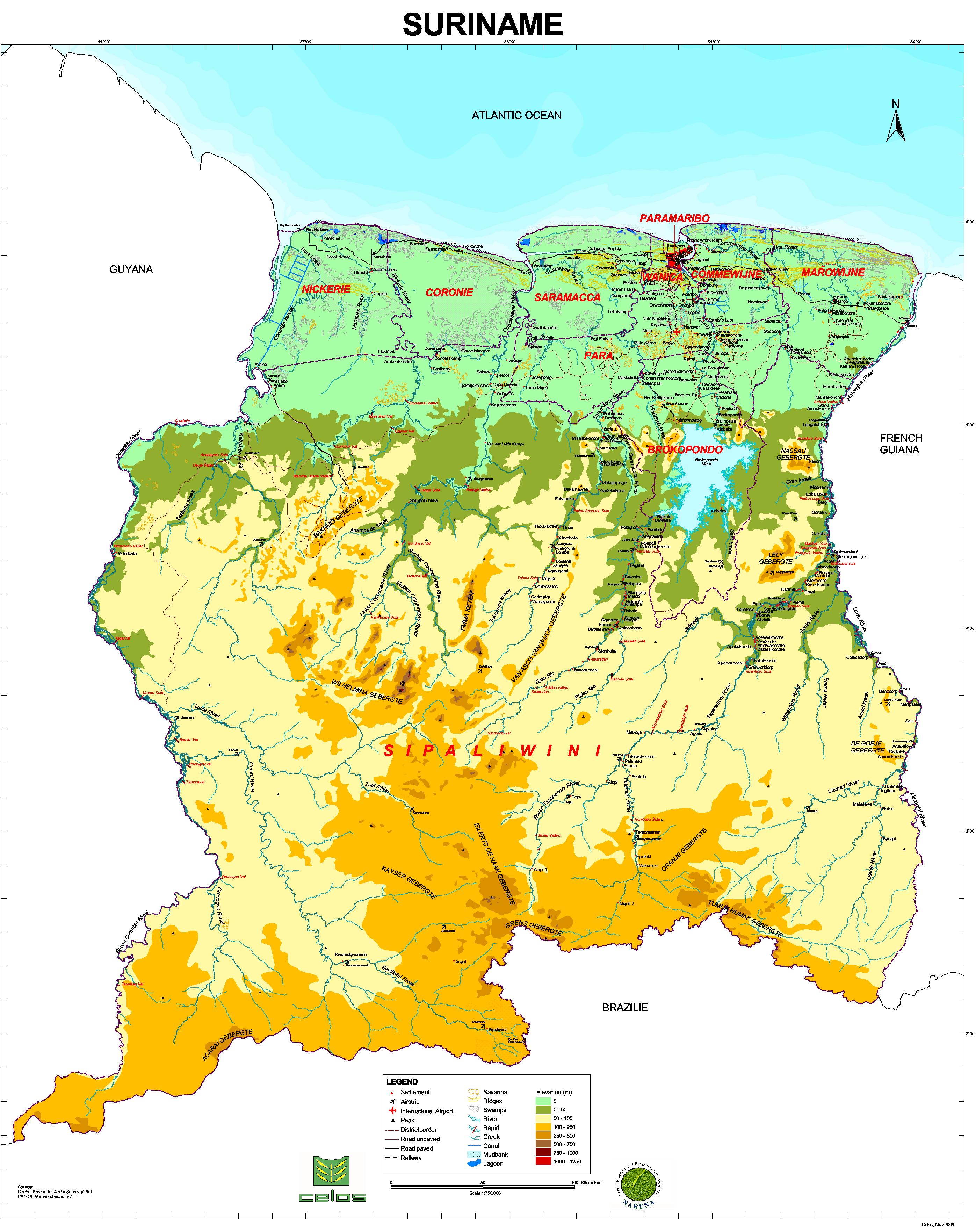
Map of Suriname
Rainfall map of Suriname
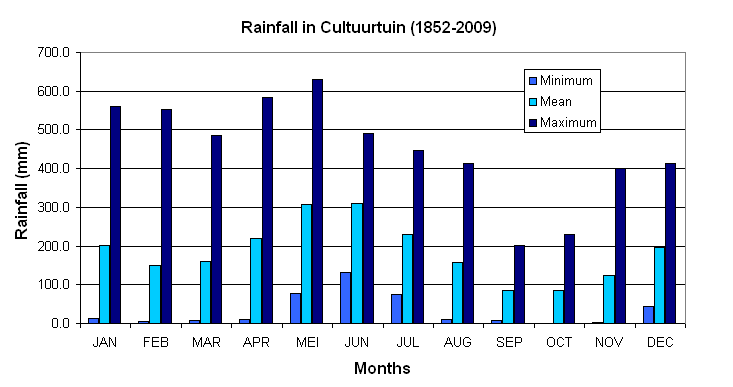
Monthly rainfall distribution in Paramaribo (station Cultuurtuin, 1852-2009)
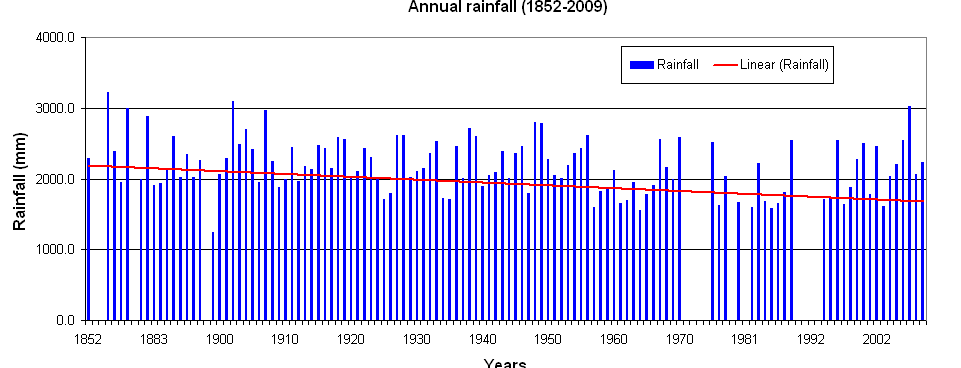
Annual rainfall trend in Paramaribo (station Cultuurtuin, 1852-2009)
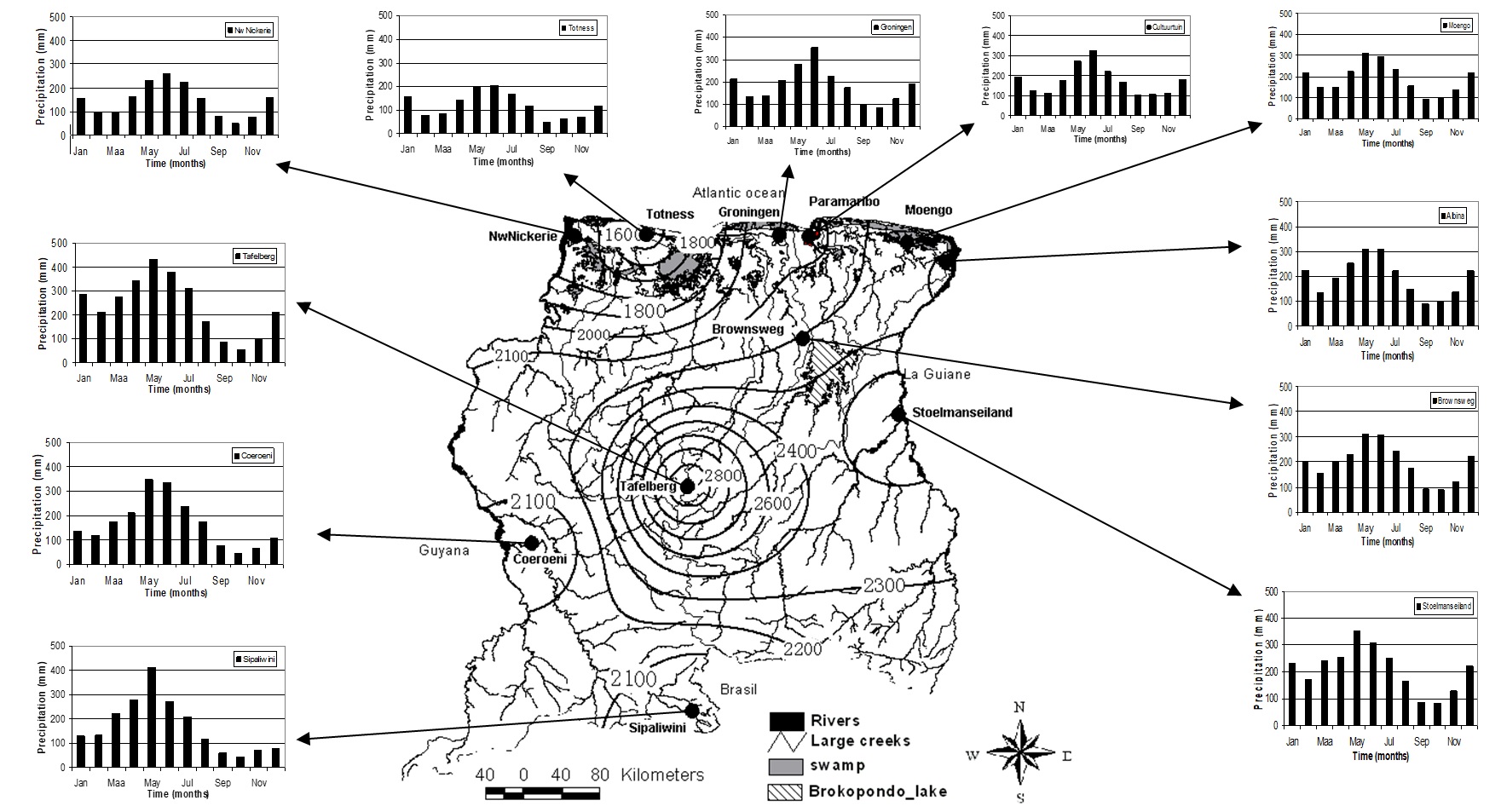
Annual and monthly rainfall distribution in Suriname (1961-1985)
Annual rainfall trend in Paramaribo (station Cultuurtuin, 1852-2009)

Suriname can mainly be distinguished by three landscapes:
- The coastal plain: the coastal plains are about 21,000 km2 and can be divided in:
- The young coastal plain (lower plain): consist of soft fluvial clays and of sand ridges. This area is lower than 6 m above mean sea level. In this area percolation and surface drainage are very slow, because of the clay and peat soils. Most water is removed by evapotranspiration.
- The old coastal plain (upper plain): consist of silt clays, loams, sandy loams and fine sand. This area lies between 6 and 12 m above mean sea level. In this area percolation and surface drainage are very slow.
- The savannah belt: consist of white coarse sands and coarse sandy clays. This area is about 8,500 km2 and lies between 15 and 20 m above mean sea level. In this area, groundwater flow is the main contributory to discharge. The period of time to peak in this area is about 6.5 to 15 hours. This area reacts more quickly to rainfall. The savannah belt is an important sources of recharge of the aquifers.
- The Precambrian shield or basement. This occupies about 80% Suriname’s landscape. Infiltration and percolation in this area is very small. Surface runoff is very high an dteh drainage density is high. Time to peak period of about 13 to 28 hours and a concentration time of 51 to 72 hours were reported in literature.
Geomorphology map of Suriname
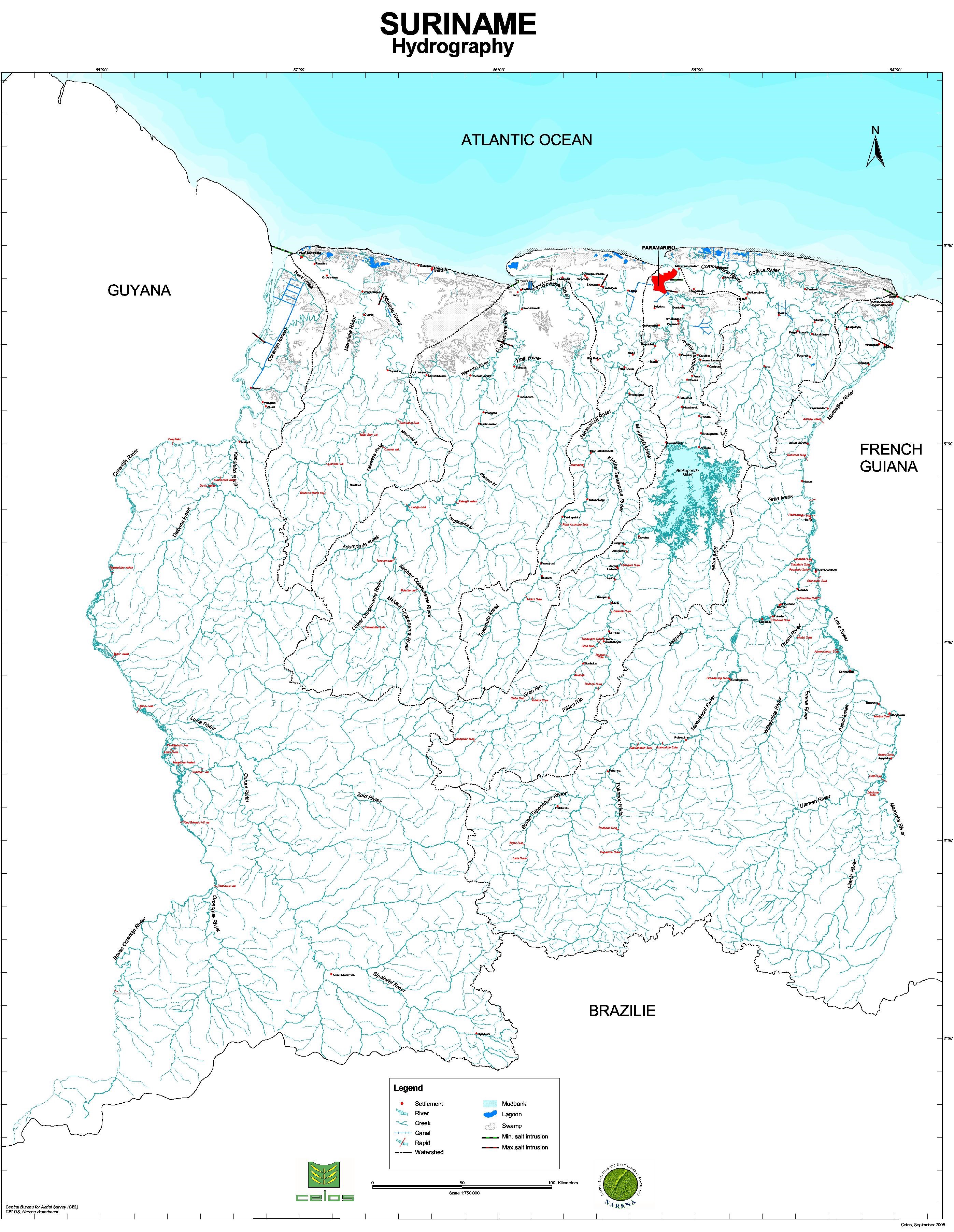
Water resources are abundant and can be found either as surface or groundwater. The total outflow into the Atlantic ocean consist of 80% of the basement area runoff (126,500 km2), 8% of the savannah area and 8% of the coastal plain areas (21,000 km2). The basement area is the major source of surface water and the savannah belt is the major source of groundwater runoff.
CONTACT
SWRIS
The SWRIS was created by the Anton de Kom University of Suriname (SMNR programme) with the support of UNDP, WWF and government authorities and is a voluntary effort on the part of the partners.
SWRIS-Secretariat
Address:
Anton de Kom University of Suriname
Leysweg, POB 9212,
Paramaribo, Suriname
Department of infrastructure
Building 16, Room 56
General phone:
+597-465558 ext 2355, 2357
APP/SMS/MOB:
+597-(0)-8500283
Email:
msc-smnr@uvs.edu
We are on social media
Copyright 2018 SWRIS | All Rights Reserved
Webdesign and development by Bit Dynamics
